M2, How To

The topic of ESG is extremely relevant for companies as it promotes their future value creation, reduces risks and strengthens the trust of stakeholders. Dietrich Bartsch, Team Lead Business Intelligence at M2, explains in a detailed article why the integration of ESG reporting has long been a strategic necessity in order to ensure long-term corporate success and a sustainable future.
This article highlights various aspects of ESG and shows why it is important for companies to address this issue. It explains the requirements for ESG reporting and outlines the procedure for preparing this report. Particular attention is paid to the technical implementation, especially the innovative ESG Flex Blueprint from M2. A comparison between this approach and other standardized ESG products is presented, including the aspects of IT security and data protection.
What does ESG mean and why is it important for companies to address it?
ESG is an abbreviation and stands for three areas in which companies can engage in sustainability.
E - Environment
S - Social
G - Governance (corporate management)
Several topics are bundled into these three areas. Here are a few examples that fall under this categorization:
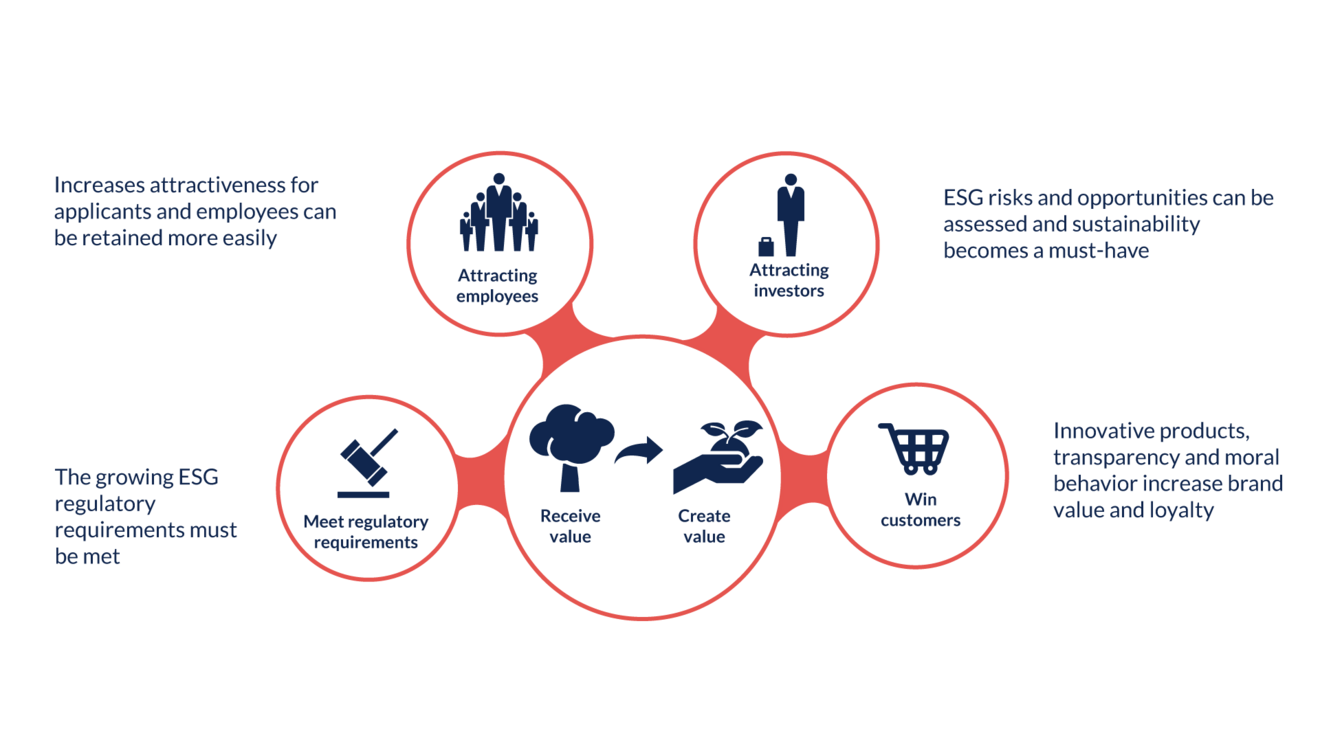
As part of the European Commission's Green Deal, sustainability has been included in the reporting (management report) of companies and your sustainability strategy is given a higher priority for your company. But the regulatory requirements are not the only reason why you should be concerned with sustainability. Investors are increasingly asking about the sustainability strategy of companies, as many investments are tied to sustainability reporting.
84% of investors actively incorporate ESG criteria into their investment decisions. In addition, companies with a good sustainability record are more attractive as employers for many applicants in a highly competitive market for skilled workers. Last but not least, customer acquisition also plays a role for companies, regardless of B2B or B2C business, as ESG reporting is also important as part of the supply chain so that the business partner can include the necessary information in their own ESG reporting. The dependence of companies on receiving ESG information from suppliers can therefore be a decisive criterion for future cooperation.
According to Prof. Dr. Rupert Felder, companies that do not deal with sustainability issues will have disappeared from the market in five years' time. In any case, sustainability must be approached as a benefit for a company and not as a charity or due to regulatory pressure.
Requirements for ESG reporting
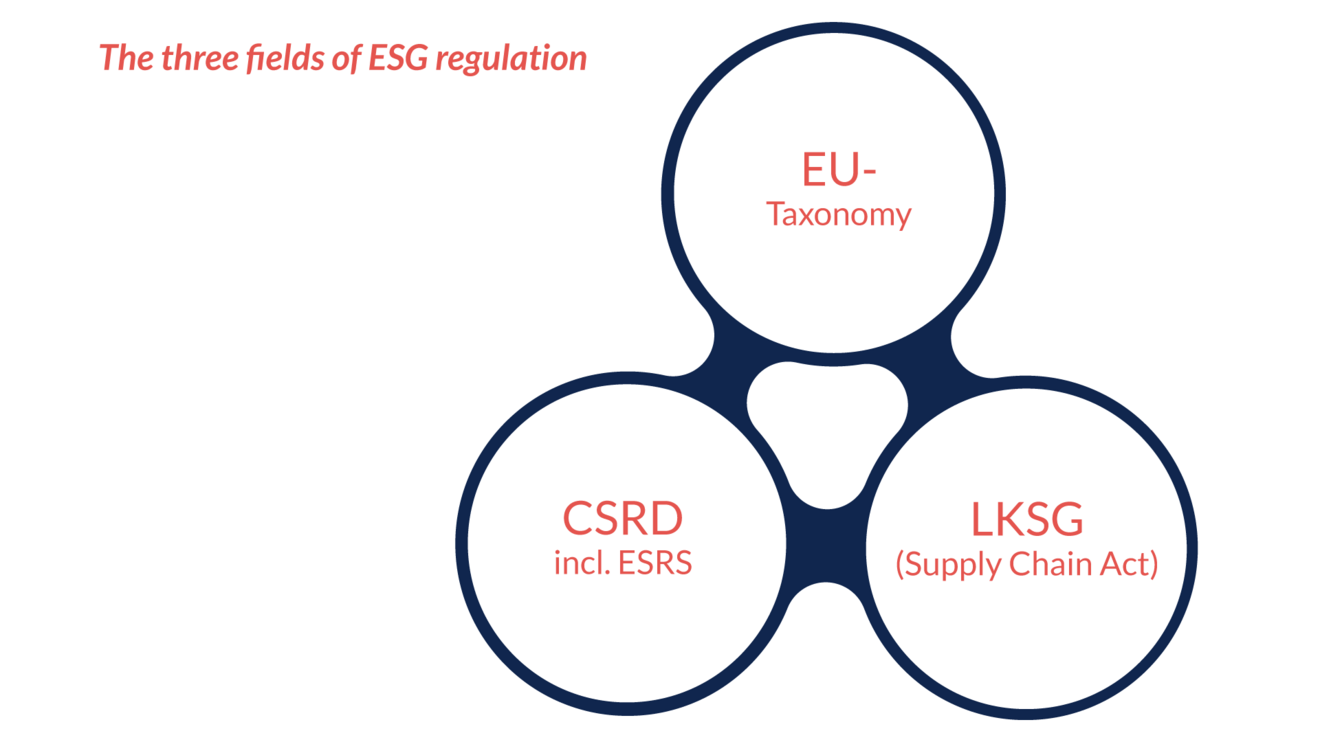
With the European Green Deal, the European Commission initiated a comprehensive program in 2019 with the aim of making the EU climate-neutral by 2050. Europe wants to be a global role model in terms of sustainability and climate focus, ultimately with the aim of steering financial flows sustainably and, above all, creating transparency. This is now being reflected in a wave of new regulation. The importance of sustainability reporting is increasing significantly and is to be placed on the same level as financial reporting in the future.
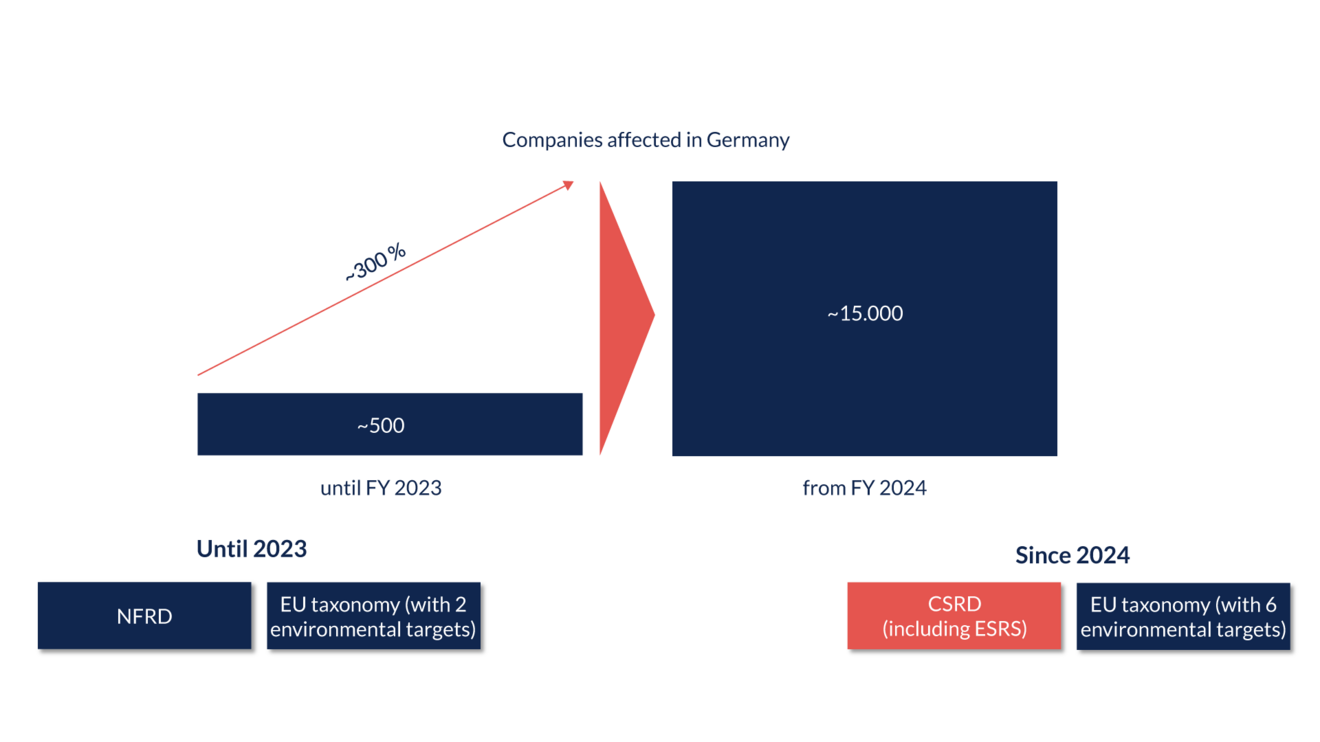
From the financial year 2024, the proportion of companies affected by the Non-Financial Reporting Directive (NFRD) will increase significantly. While around 500 companies had to publish a sustainability report until 2023, around 15,000 companies across Germany and 50 million companies across Europe will now be affected from 2024. In addition, the EU taxonomy, which contained two environmental targets until 2023, will be expanded to include four more environmental targets.
But why is the number of companies rising so sharply? The number of employees, turnover and total assets play a key role here. Until 2023, the Non-Financial Reporting Directive (NFRD) was only mandatory for capital market-oriented companies with more than 500 employees. It therefore only applied to companies that were listed on the EU stock exchange, operated as a credit institution or as an insurance company.
This is now being replaced by the CSRD, which will be mandatory from 2024 for large capital market-oriented companies that were previously subject to the NFRD. From 2025, all large companies will be affected that, regardless of their capital market orientation
- have a number of employees of 250 or more
- achieve a turnover of € 50 million or more
- have a balance sheet total of € 25 million or more
The principle applies here that if two of these three criteria are met, the CSRD is mandatory.
From 2026, publicly traded small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) will also be affected.
In addition, these companies must also comply with the EU taxonomy and report on this in the management report. From 2024, this will affect all six of the EU's environmental objectives; in contrast, previously only compliance and activities in the area of climate protection and adaptation to climate change had to be reported on.
In addition, there is the Supply Chain Due Diligence Act (LKSG). The aim of this law is to improve the protection of human rights and the environment in global supply chains. The law sets out clear and enforceable requirements for companies' due diligence obligations and creates legal certainty for companies and those affected. The LKSG already affected companies with more than 3,000 employees in Germany in 2023 and has now also affected companies with 1,000 employees since 2024. However, companies can also benefit from synergy effects with CSRD reporting.
This wide range of measures is intended to create incentives so that companies can take responsibility for the impact of their business activities on the environment and society and commit to a more sustainable future.
The issue of sustainability should therefore not be viewed purely from a regulatory perspective. These regulatory requirements should always be seen as an opportunity to develop one's own company profitably.
What is the procedure for preparing the ESG report?
What a company must report is defined in the European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS). These companies are obliged to publish this information in their management report. CSRD reporting must comply with the ESEF standard, the uniform EU standard for the electronic reporting format.
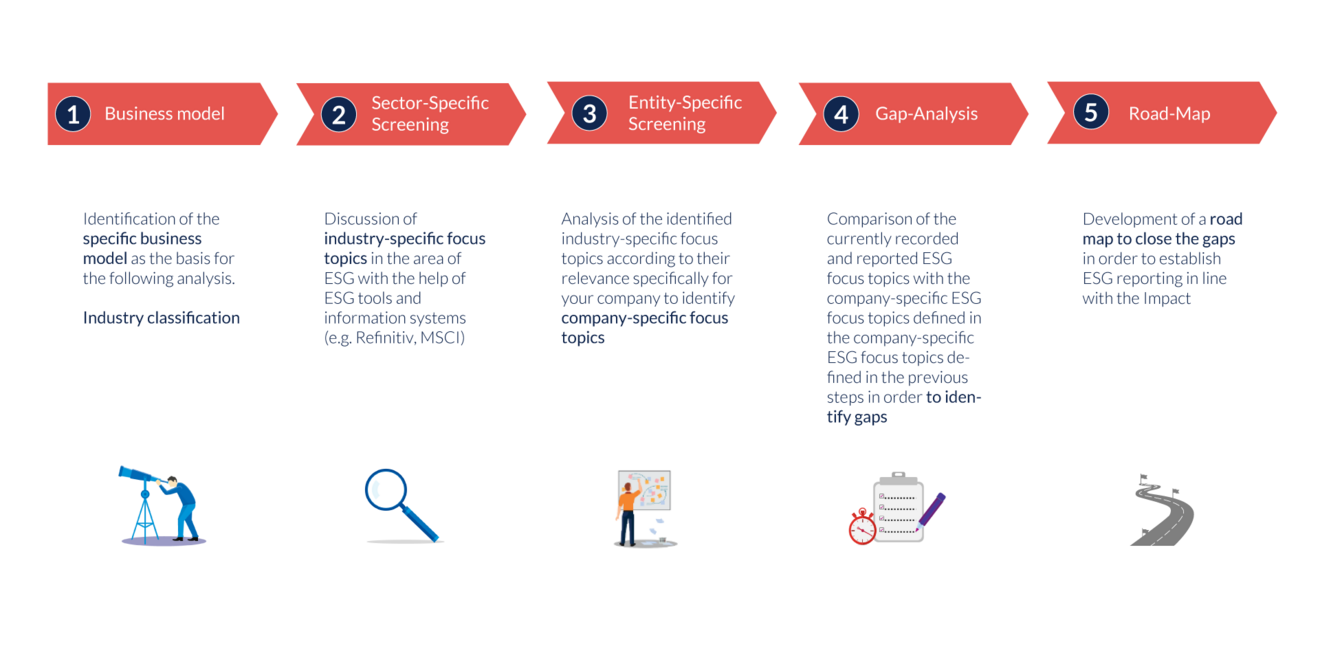
Key figures that are essential for the company and its business operations must be reported. In order to evaluate these key figures, we analyze in several steps how to define these key figures for your company.
Technical implementation: The M2 ESG-Flex-Blueprint
But how can such a complex topic be implemented technically? There are currently many off-the-shelf solutions on the market that appear to meet the requirements and with which you can presumably create your ESG reporting very quickly and easily. However, in our experience, we have been approached by companies that initially invested in these solutions but then needed further support because they could not fully cover the topic on their own and without external help.
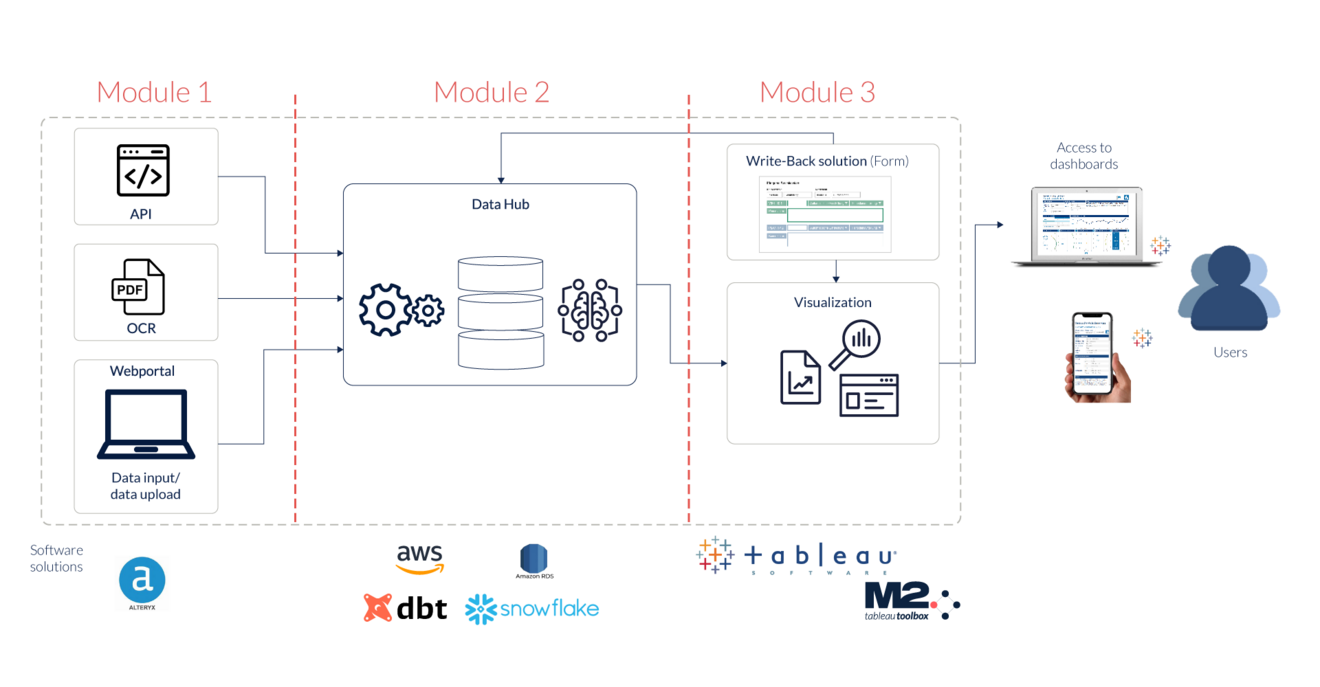
Our solutions start with a comprehensive consultation to better understand your target picture and actually meet your requirements. The topic of ESG cannot be met with standard solutions. The requirements are too specific for each industry and company. We work with you to develop a target image that meets your requirements. Our modular approach is a good way to deal with a core topic depending on the focus, whereby the other modules can be added flexibly at an earlier or later stage. This is why we call the model ESG-Flex-Blueprint.
Module 1:
This module deals with data acquisition. Data can be read in different ways. Three methods are possible to capture all the necessary data points:
- The direct interface to the data source (API), which can be used to automatically retrieve data directly.
- The OCR method for reading PDF documents, which is used to capture contracts or other relevant company documents.
- Data input or data upload, where suppliers or individual departments can store their information conveniently and in a targeted manner.
Here we also work together with software solutions such as Alteryx for development, but the tool decision should be of secondary importance.
Module 2:
This module contains the data transformation. Here, the source data is prepared in three steps in a robust data environment, processed using the necessary logic and converted into the target format using data science and AI. This corresponds to the current standard of data transformation in the ELT process (Extract - Transform - Load).
Stage 1: The raw data is stored in versioned form.
Stage 2: After initial processing of the raw data and enrichment with additional mapping data / dimensions, this data is available for refinement.
Stage 3: After checking and refining the data from stage 2, the final data is stored in a reporting format.
As can be seen in the diagram, we use our software partner AWS and dbt as a transformation tool. This proposal should be compared with your IT technology in advance.
Module 3:
The visualization of the data is the target screen for the end user to read and evaluate the final data. But a dashboard is not only important for the final data: appropriate monitoring is also useful for checking the incoming raw data, for validating and checking the completeness of this data. Using the Form Builder developed by M2, a write-back solution, refinements to the data can be easily implemented in a dashboard and written back to the database.
M2 has many years of experience in the development of dashboards, which we have implemented with our software partner Tableau.
Comparison between M2 ESG flex blueprint and off-the-shelf ESG products
The ESG flex blueprint offers a number of advantages over off-the-shelf solutions currently available on the market. Here is a brief comparison:

Depending on your requirements, an off-the-shelf product may be a good choice. As you can see in this table, there are certainly good reasons to opt for one or the other approach.
IT security and data protection
IT security and data protection is an important topic for our customers, especially in Germany. With our experience in setting up and operating cloud infrastructure environments, we can provide you with the necessary answers to security-related issues.
With certifications in accordance with the FIPS 140-3 standards for encryption technology (key management system) and the provision of cloud solutions in accordance with the BSI IT Grundschutz standard, our solutions meet the necessary security requirements that generally apply to standard solutions in privately managed companies, but which we also apply to government bodies and institutions.
Procedure and offer from M2
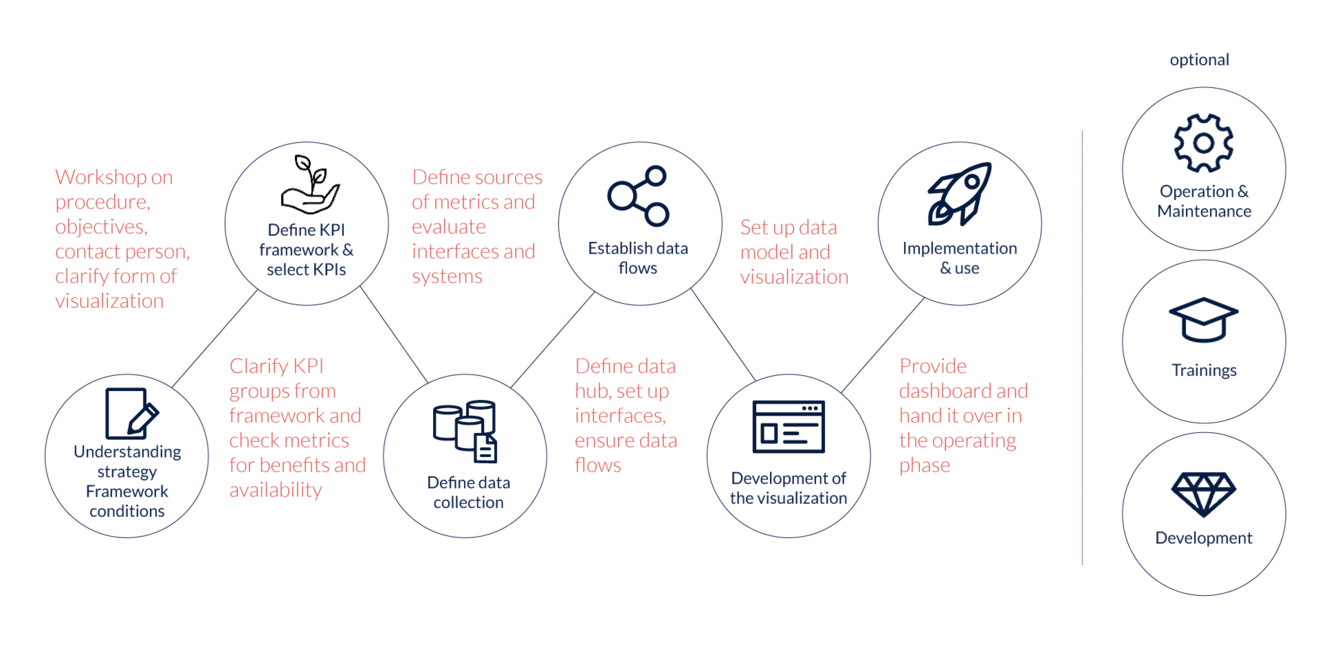
The approach taken by M2 and its partners in setting up the ESG standard is divided into several points:
- Building an understanding of strategy and framework conditions
- Define KPI framework and select KPIs
- Define data collection
- Establish data flows
- Develop the visualization
- Implementation and use
We offer our customers the option of
- Operation and maintenance
- Training courses
- Further development of the environment
M2 offers a variety of services for your sustainability reporting and supports you to do it right, providing a sustainable solution that will not only help your company create its first report today, but will continue to be a good solution for your company in the future.
Contact us today to navigate together into a data-driven future. As your trusted partner, we will be with you every step of the way.

The article was written by Dietrich Bartsch, Team Lead Business Intelligence at M2